What is ITIL?
ITIL offers a framework of structured, scalable best practices and processes that organizations can adopt and adapt to fit their own operations. Organizations implement ITIL best practices to improve service. Cost benefits are an added benefit due to streamlined processes. When fully implemented, the processes ensure consistent, high quality service that meets business needs.
Implementing ITIL is not a quick fix nor will it be easy. It takes a lot of thought, commitment and hard work to successfully change the way the IT organization does business. There will be things that you do today that you will not do afterwards and vice-versa. Most people will continue to do what they do today but using more repeatable processes and in doing so they will improve service delivery, becoming more productive.
The History of ITIL
Developed in the early 1990s by the British government, the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) has gone through two subsequent revisions, each revision having a different perspective on IT service management. The initial offering spanned 42 volumes covering a wide range of IT best practices, from customer engagement to under floor cabling.
By the mid-1990s, ITIL had become the world-wide de facto standard for IT best practices. Early adopters enjoyed their benefits but soon realized there needed to be some rigor around them in order to provide better-managed IT services.
Generally your IT organization’s culture and maturity will dictate the version that provides the greatest benefits. More mature organizations with existing strong business-unit involvement can derive more benefits with Version 3, while the technology best practices can help less mature organizations. There is no work lost if you start with Version 2 as all the processes and best practices are easily transferrable to Version 3.
The first revision of ITIL, known as Version 2, took a technology-oriented perspective to coordinate and integrate the best practices. Organizations with less mature IT management processes might want to start with this version of ITIL.
The current revision, Version 3, takes a service management lifecycle approach, managing the development and delivery of IT services from a business perspective. Version 3 is more likely to appeal to organizations that manage IT from a business-value point of view.
Benefits of ITIL Implementation
Organizations implement ITIL best practices to improve service; however, they also enjoy the cost benefits from improved productivity as a result of streamlining work processes. When fully implemented, the processes ensure consistent, high quality service that meets business units' needs. Services become more focused on the business than technology.
Other benefits to embracing ITIL best practices include:
Better managed IT costs
- People are more productive because only authorized work is performed.
- Service quality improvements result in fewer services anomalies, eliminating staff distractions and permitting more work directly benefiting business to be performed.
- Trade-offs between costs and levels of IT service are better understood, permitting more informed business decisions, fostering a much closer partnership between business and IT.
- Built-in continuous improvement processes ensure that business applications operate efficiently. Through the use of the processes, performance improvement opportunities are identified and ITIL processes guide how corrective work is commissioned and implemented.
Better understanding between IT and business
- IT services and the resources needed to support them are better understood by the business, and IT better understands the day-to-day business processes IT supports.
- The IT organization is structured with an enterprise view so it is easier to see and maintain services from an end-to-end business perspective.
- Meaningful and measurable service metrics gauging IT service performance are in place and well-communicated.
More efficient organization
- IT has a well-defined structure with clearly defined roles and responsibilities, improving efficiency.
- Clearly defined processes and procedures simplify IT change management and provide a common point of reference for internal communications.
- All IT processes are standardized and integration points and hand-offs are well documented and understood.
- Duplication of effort by different departments is uncovered and eliminated.
ITIL Versions
Implementing an ITIL practice is all about IT service optimization. So far, two versions exist: ITIL Version 2 and ITIL Version 3. Both versions are beneficial, and which one you implement will depend on your business’s IT maturity.
ITIL Version 2
Version 2 focuses on the categories and areas that make up a service optimization practice.
ITIL Business Relationship Management

ITIL business relationship management is a group of people that serve as liaisons between the business and IT. This is where business requirements are gathered and translated into IT resource requirements.
ICT Infrastructure Management

Information and communication technology (ICT) infrastructure management is the intermediary between service management and technology. It’s the branch of ITIL that focuses on processes.
The goal of ICT infrastructure management is to use proven, repeatable processes to provide a stable operating environment for everyone using the technology.
Application Management

Simply put, application management is the process of managing applications throughout their lifecycle.
Traditional application management processes guide how business applications are developed, managed, improved, and—when necessary—retired.
Security Management

Security Management is an integral part of the other IT disciplines. It has both a business and service focus to ensure the organization will meet regulatory agency requirements, such as Sarbanes-Oxley, FDIC, SEC, or HIPAA.
ITIL Service Delivery

Service Delivery is the delivery of an IT service to a customer. Service Delivery brings the business and IT together to benefit the company as a whole—eliminating the detrimental “Us-versus-Them” mindset.
This is important because it performs a service the customer cannot do—and provides great value. Service Delivery should foster a corporate behavior for responsible use of IT services while maximizing corporate profits.
ITIL Service Support
ITIL service support encompasses the support processes necessary to ensure service quality. These processes manage problems and changes in the IT Infrastructure and are more control-oriented than technical in nature.
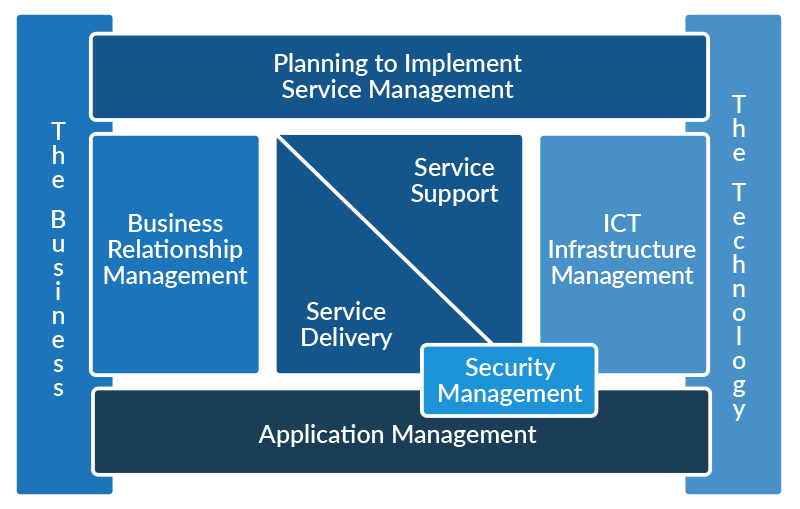
Components of ITIL Version 2 Service Delivery
ITIL Version 3
Version 3 is a next step towards mature, continuous IT service optimization.
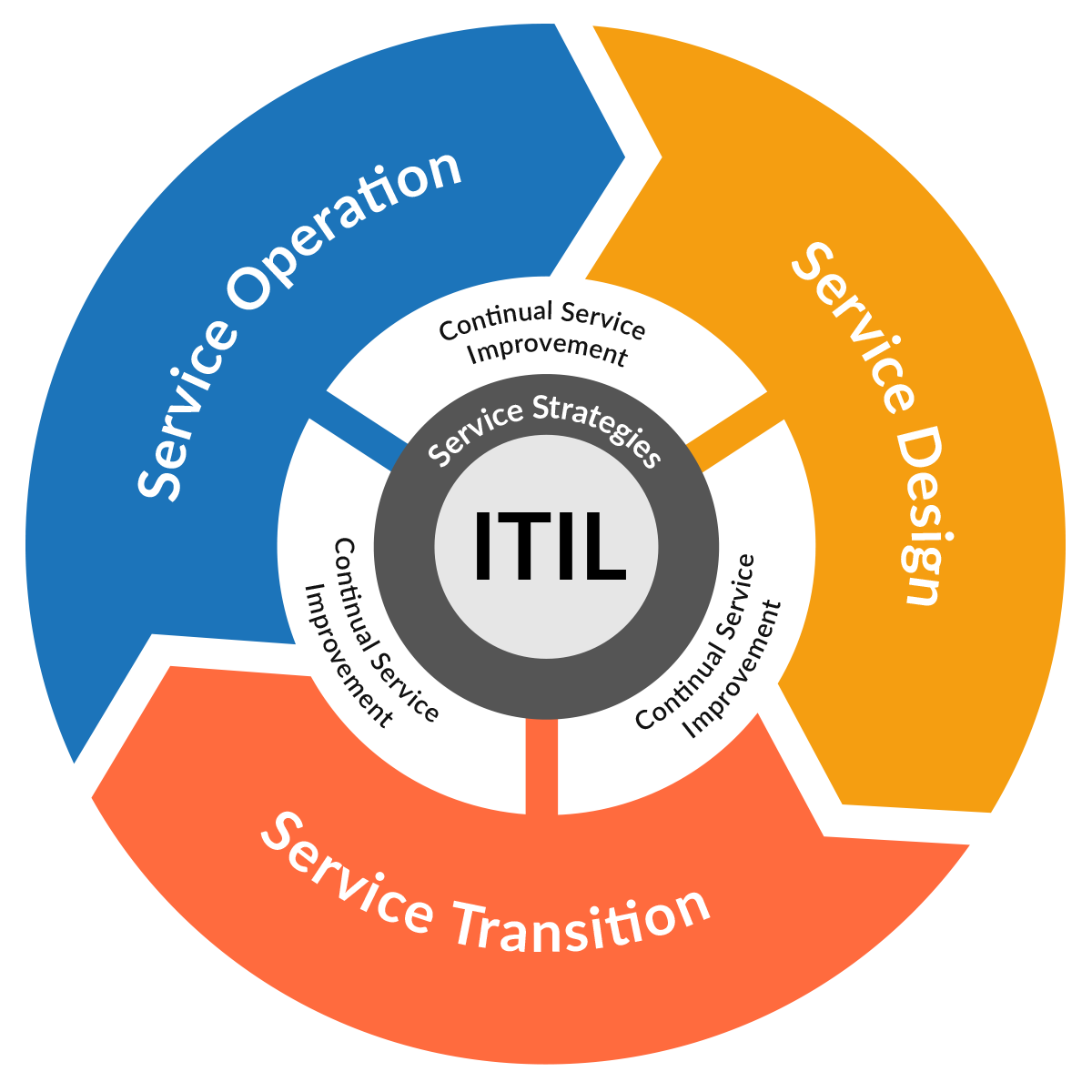
The first revision of ITIL, known as Version 2, took a technology-oriented perspective to coordinate and integrate the best practices. Organizations with less mature IT management processes might want to start with this version of ITIL.
The current revision, Version 3, takes a service management lifecycle approach, managing the development and delivery of IT services from a business perspective. Version 3 is more likely to appeal to organizations that manage IT from a business-value point of view.
Generally your IT organization’s culture and maturity will dictate the version that provides the greatest benefits. More mature organizations with existing strong business-unit involvement can derive more benefits with Version 3, while the technology best practices can help less mature organizations. There is no work lost if you start with Version 2 as all the processes and best practices are easily transferrable to Version 3.
ITIL FAQs
ITIL can be an overwhelming and daunting proposition. Questions abound as we work to grasp what an ITIL implementation really means for our own organizations. We address some of the common questions here.
Getting Started
Take the Next Step
Read the guide:
Explore the software:
Watch a Demo > Product Info >
Continue Learning
ITIL Components:
Business Relationship Management
ICT Infrastructure Management
Application Management
Security Management
Service Delivery
- Service Level Management
- Financial Management
- Capacity Management
- Availability Management
- Continuity Management
Service Support
- Incident Management
- Problem Management
- Configuration Management